The V-belt is a large class of transmission tapes. It is named after the isosceles trapezoidal section. It has developed rapidly since the advent of the last century and can replace mechanical gear transmissions. The V belt is widely used for power transmission of electric motors and internal combustion engines. This is because it is continuously improved in terms of material, structure and shape, and combines many advantages such as high power, high speed, small deformation, long life and small space.
With the diversification of the use requirements, the classification of V-belts is also increasing day by day. According to the belt structure, there are edging and trimming points; according to the core structure, there are disc cores and wire cores; depending on the application, there are industries. , the agricultural machinery industry and the automotive industry; according to the shape of the broken (cut) face, there is a wide and narrow difference. According to the shape of the section, it can be divided into the following three types.
(1) ordinary V belt
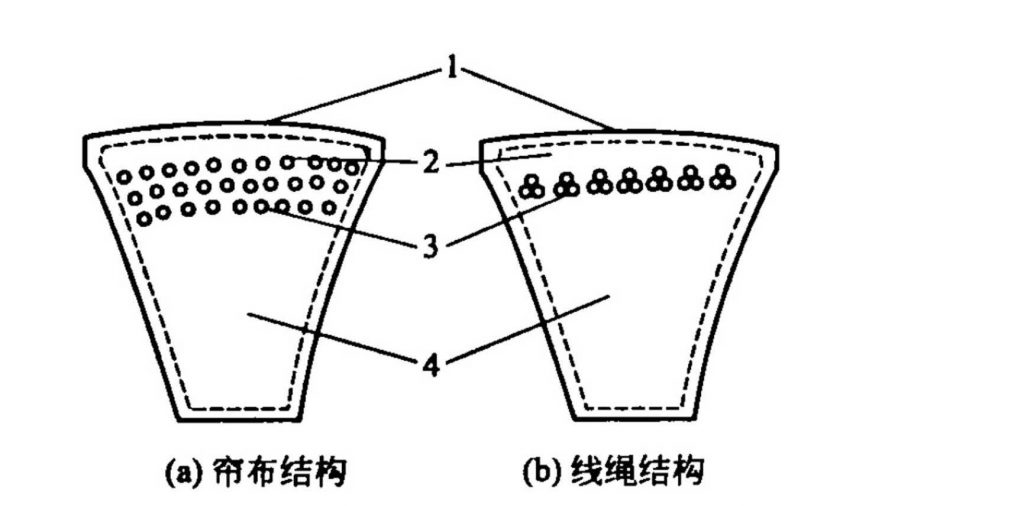
The ratio of the section height/top section width of the ordinary V-belt is 0.7, and the wedge angle is 40°, which is suitable for general mechanical transmission, but is not suitable for use in automobiles and agricultural machinery. It consists of a top coat, a top coat, a strong (stretch) layer (raw curtain or cord) and a primer (compressed) layer (see Figure 6·IO). O strength layer material is divided into two types: wire and cord. The advantages of the wire structure include relatively high flexibility, no quality problems such as interlayer displacement and delamination, but the wire rope V-belt of the same specification is not as strong as the V-belt of the cord. The section specifications are divided into 0, A.E, C, D, E, F and other models from small to large.
All kinds of V belts can be made into a single root, that is, the molding to vulcanization is carried out separately, which is called a cloth type; or the cylindrical shaped embryo can be formed first, and then vulcanized and then cut into a single root, which is called a cutting belt. From the appearance, the entire body of the former is covered with a cloth without being exposed, and the sides of the latter are exposed. The production efficiency of the dicing tape is high, but the reinforcing layers on both sides are exposed, and the fiber ends are prone to disorder.
(2) Narrow V-belt
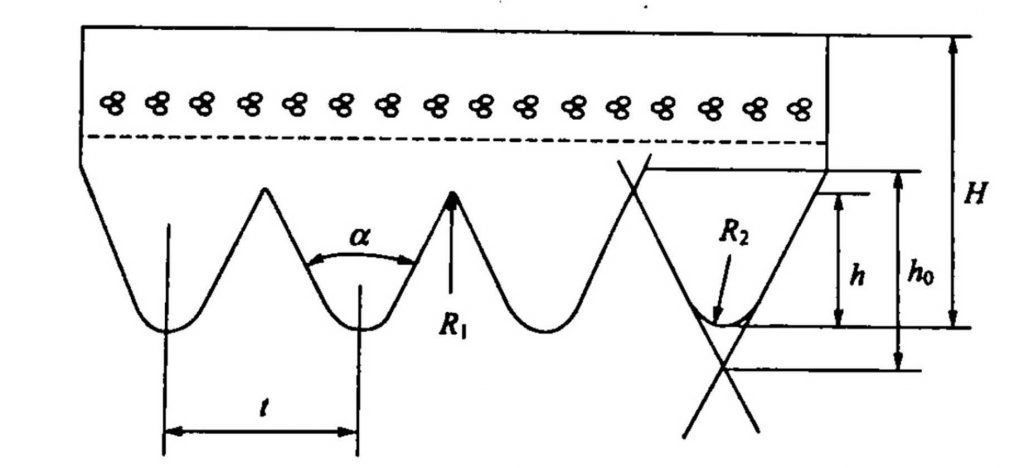
The shape parameters of the section are different from those of the ordinary: the aspect ratio of the section is 0·9, which is higher than 0.2 of the ordinary V-belt, and the appearance is obviously narrow.
This structural feature gives it the following performance characteristics:
1 higher transmission power, 0.5-1.5 times higher than the V-belt of the common structure;
2 The structure is compact and 50% smaller than the ordinary structure;
3 line speed is high, up to 40~50m∕s, suitable for high speed operation;
4 The center distance of the transmission wheel and the width of the wheel groove can be reduced to make the overall transmission system more compact.
(3) Wide V belt
The wide V-belt refers to a flat V-belt with a height/width ratio of only about 0.3. It is usually used in a belt-type transmission. Therefore, it is also called a variable-speed V-belt, which is developed rapidly due to smooth transmission, convenient maintenance, and low manufacturing cost. In order to meet the needs of shifting, the top and bottom surfaces can also be toothed to improve the engagement with the drive wheel.