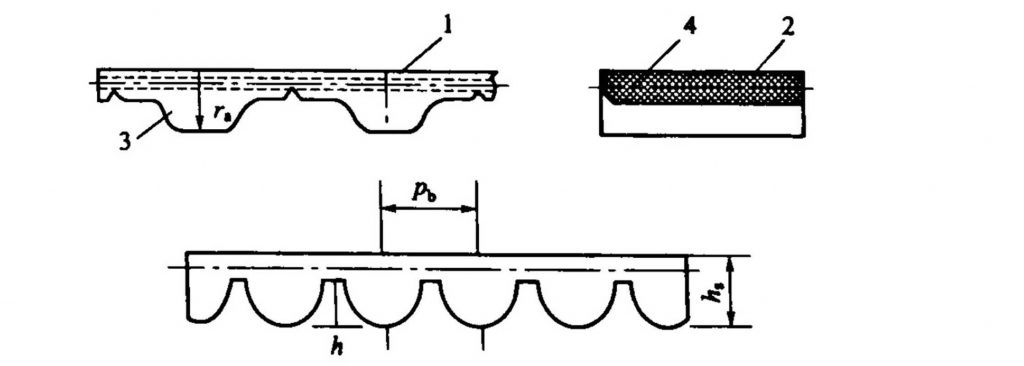
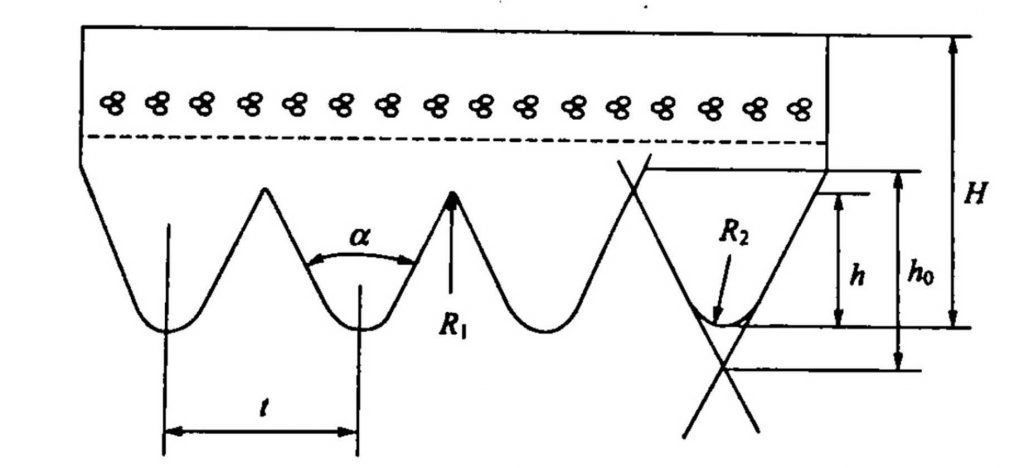
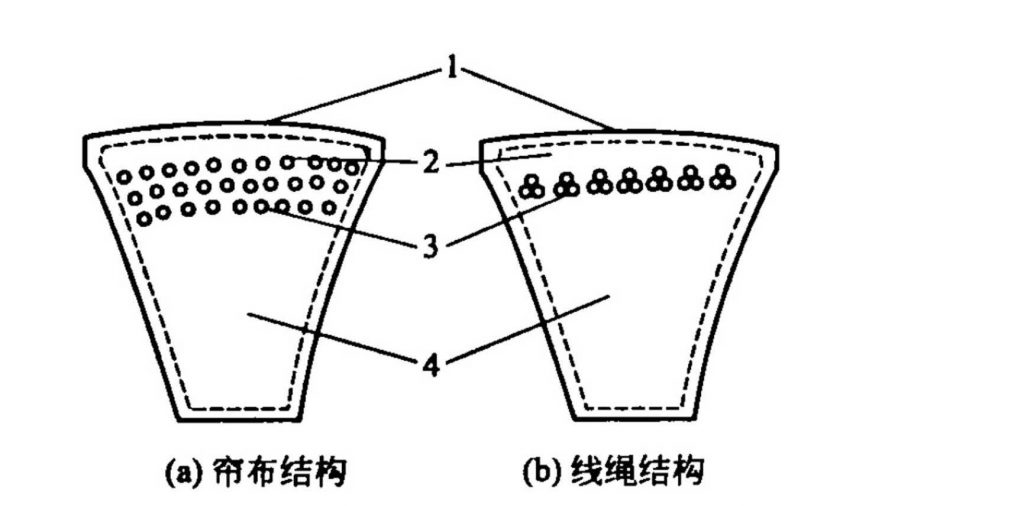
The classification of petroleum resin products is more complicated than other resins commonly used in rubber, because it has many raw materials and can be flexibly selected in terms of raw material selection and manufacturing process in order to meet different usage environments and requirements.
Divided by raw materials, they can usually be divided into three categories.
- The aromatic petroleum resin is subjected to self-polymerization or block copolymerization under the action of a catalyst by using a petroleum-cut fraction raw material. Different catalytic systems can be employed depending on the polymerization process. The properties of the resulting resins may vary widely due to the different components involved in the reaction.
After adding such petroleum resin to the rubber grommets raw material, the hardness and the tensile stress are improved, and the anti-aging property is better. The comparison data before and after aging is stable and uniform. The wear resistance and tear resistance can be increased by 20% after adding the resin, which is very beneficial for rubber grommets.
- The petroleum resin and the rubber of the aliphatic petroleum resin have good compatibility, but because of its high content of diene and high degree of unsaturation, the thermal stability is poor, but the viscosity increasing effect is superior to that of the ancient Malone resin.
This type of resin is obtained by the dispersion of C5, a by-product of ethylene cracking, and is mainly composed of a trans structure. It is obtained by anionic polymerization under the catalysis of a Lewis acid.
- Block copolymerized petroleum resin This is a third type of petroleum resin other than the above two types, which is a regular block copolymer of an aromatic fraction and an isoprene monomer. The order of the block copolymerized petroleum resin structure is similar to that of thermoplastic SBS, which is polymerized by initiation of an anionic catalyst. The advantage of this product is that it is suitable for two elastomer materials with widely different polarities, which integrates the elastomer materials which were impossible to blend, which simplifies the production process of rubber grommets and promotes the complementary performance between them.