The rubber synchronous toothed belt is named for the high synchronization between the belt body and the transmission wheel, referred to as the timing belt. It combines the lengths of different transmission methods (gears, chains and tapes) to reflect high efficiency, stability, low noise, no lubrication and many other advantages. All of this comes from the precise engagement between the toothed body of the working face and the drive wheel groove. Therefore, during the transmission process, there is no relative slip between the belt body and the transmission wheel, so that the synchronous transmission can be realized at any instant.
Variety
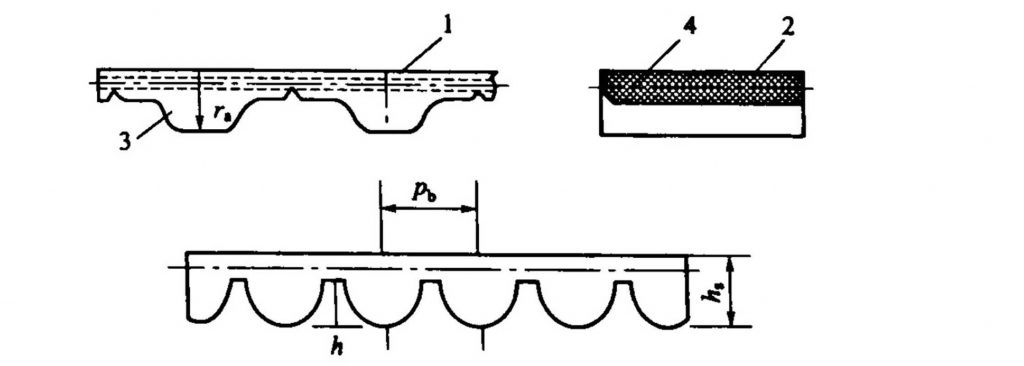
According to the shape of the tooth body, it is divided into two types: a trapezoidal timing belt and an elliptical timing belt. The former (Fig. 6·12 left) is the earliest conventional variety, with its tooth body showing a large and small trapezoidal shape. The latter (Fig. 6-12 right) appeared in the 1970s, and the tooth body has a circular arc shape. Compared with the trapezoidal timing belt, it can withstand greater torque.
Trapezoidal timing belt and elliptical timing belt
Later, in order to adapt to the emergence of multi-axis transmission, a double-sided timing belt was derived, and the pitch, the tooth shape and the timing belt of the single-sided transmission were the same. The difference is that the upper and lower teeth have teeth, and they are arranged in two ways: symmetry and staggering.
Structure
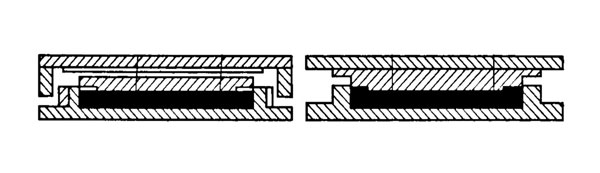
It usually consists of a rubber layer (backing), a strong layer (skeleton layer), a toothed layer and a covering layer.
Raw materials
(1) Adhesive layer
The backing layer can be made from dry glue (usually neoprene) or from liquid polyurethane (crosslinked to solid).
(2) Power layer
The strength layer is usually made of synthetic fibers, such as nylon, polyester, aramid yarn, cord, glass fiber and steel wire.
(3) tooth body
The tooth composition is identical to the adhesive layer.
(4) Cover layer
The cloth layer is a hanging rubber canvas.